A linked list of length n is given such that each node contains an additional random pointer, which could point to any node in the list, or null.
Construct a deep copy of the list. The deep copy should consist of exactly n brand new nodes, where each new node has its value set to the value of its corresponding original node. Both the next and random pointer of the new nodes should point to new nodes in the copied list such that the pointers in the original list and copied list represent the same list state. None of the pointers in the new list should point to nodes in the original list.
For example, if there are two nodes X and Y in the original list, where X.random --> Y, then for the corresponding two nodes x and y in the copied list, x.random --> y.
Return the head of the copied linked list.
The linked list is represented in the input/output as a list of n nodes. Each node is represented as a pair of [val, random_index] where:
val: an integer representing Node.valrandom_index: the index of the node (range from 0 to n-1) that the random pointer points to, or null if it does not point to any node.Your code will only be given the head of the original linked list.
Example 1:
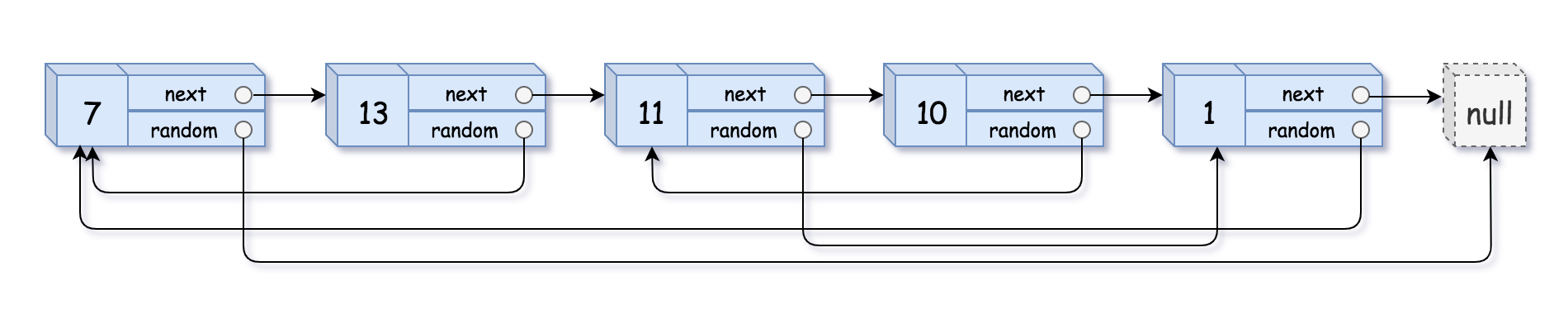
Input: head = [[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]] Output: [[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]]
Example 2:
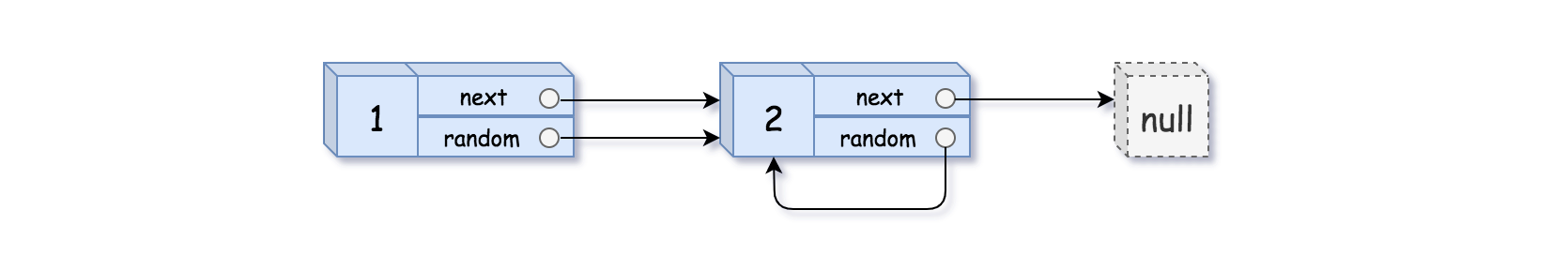
Input: head = [[1,1],[2,1]] Output: [[1,1],[2,1]]
Example 3:
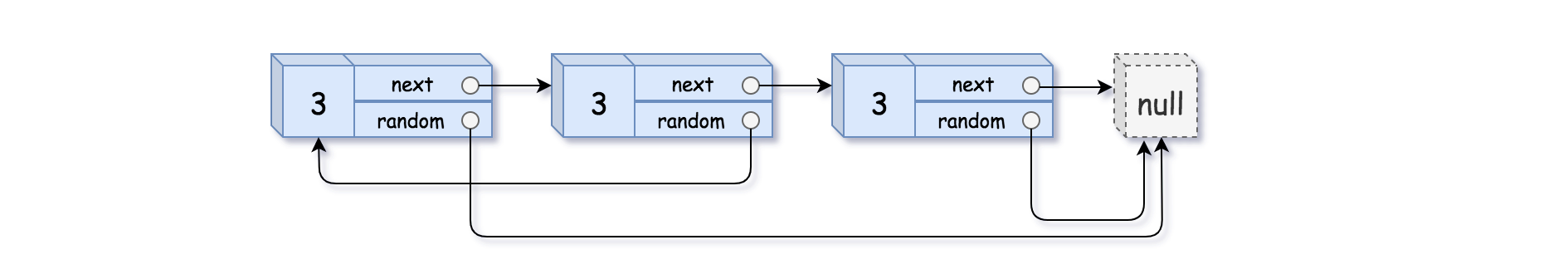
Input: head = [[3,null],[3,0],[3,null]] Output: [[3,null],[3,0],[3,null]]
Example 4:
Input: head = [] Output: [] Explanation: The given linked list is empty (null pointer), so return null.
Constraints:
0 <= n <= 1000-10000 <= Node.val <= 10000Node.random is null or is pointing to some node in the linked list.Your algorithm should run in O(n) time and use O(1) extra space.
The core challenge of this problem is to create a deep copy of a linked list where each node has an additional random pointer. The deep copy should be a completely new list with no shared references to the original list. This problem is significant in scenarios where data integrity and isolation are crucial, such as in cloning complex data structures or undo mechanisms in applications.
To solve this problem, we can break it down into three main steps:
We create a new node for each original node and insert it right after the original node. This way, the list will look like: original1 -> copy1 -> original2 -> copy2 -> ...
For each original node, we set the random pointer of its copy to the copy of the original node's random pointer. This can be done by accessing the next node of the original node's random pointer.
Finally, we separate the interwoven list into the original list and the copied list by adjusting the next pointers accordingly.
// Definition for a Node.
function Node(val, next, random) {
this.val = val;
this.next = next;
this.random = random;
}
function copyRandomList(head) {
if (!head) return null;
// Step 1: Interweave the original list with copied nodes
let current = head;
while (current) {
const newNode = new Node(current.val, current.next, null);
current.next = newNode;
current = newNode.next;
}
// Step 2: Assign random pointers for the copied nodes
current = head;
while (current) {
if (current.random) {
current.next.random = current.random.next;
}
current = current.next.next;
}
// Step 3: Separate the interwoven list into original and copied lists
current = head;
const newHead = head.next;
while (current) {
const copy = current.next;
current.next = copy.next;
if (copy.next) {
copy.next = copy.next.next;
}
current = current.next;
}
return newHead;
}
The time complexity of this algorithm is O(n) because we traverse the list a constant number of times. The space complexity is O(1) extra space because we are not using any additional data structures that grow with the input size.
null.null.To test the solution comprehensively, consider the following test cases:
When approaching such problems, it's essential to break down the problem into smaller, manageable steps. Visualizing the problem with diagrams can also help in understanding the relationships between nodes. Practice similar problems to improve your problem-solving skills.
In this blog post, we discussed how to create a deep copy of a linked list with random pointers in JavaScript. We broke down the problem into manageable steps, provided a detailed algorithm, and analyzed its complexity. Understanding and solving such problems is crucial for developing robust and efficient algorithms.
Our interactive tutorials and AI-assisted learning will help you master problem-solving skills and teach you the algorithms to know for coding interviews.
Start Coding for FREE